When developing a stainless steel water bottle, drinkware manufacturer prioritize durability and long-lasting performance. The ceramic coating on these bottles enhances both aesthetic appeal and protection against wear and tear, directly influencing the bottle’s overall longevity and functionality. This article outlines tests designed to assess the quality of ceramic coatings on insulated water bottles.
It also provides an overview of test standards and methods, which are essential for manufacturers to ensure the quality and durability of their ceramic-coated products. The laboratory conducting these tests must be properly equipped to perform them accurately and reliably.
Test Equipment
-
3M-897 Scotch tape
-
Cross-cut adhesion tester
-
STAEDTLER pencil 6H
-
300g±1g steel ball
-
Measuring tape
-
Ice maker
Adhesive Strength Test
Operating Procedures
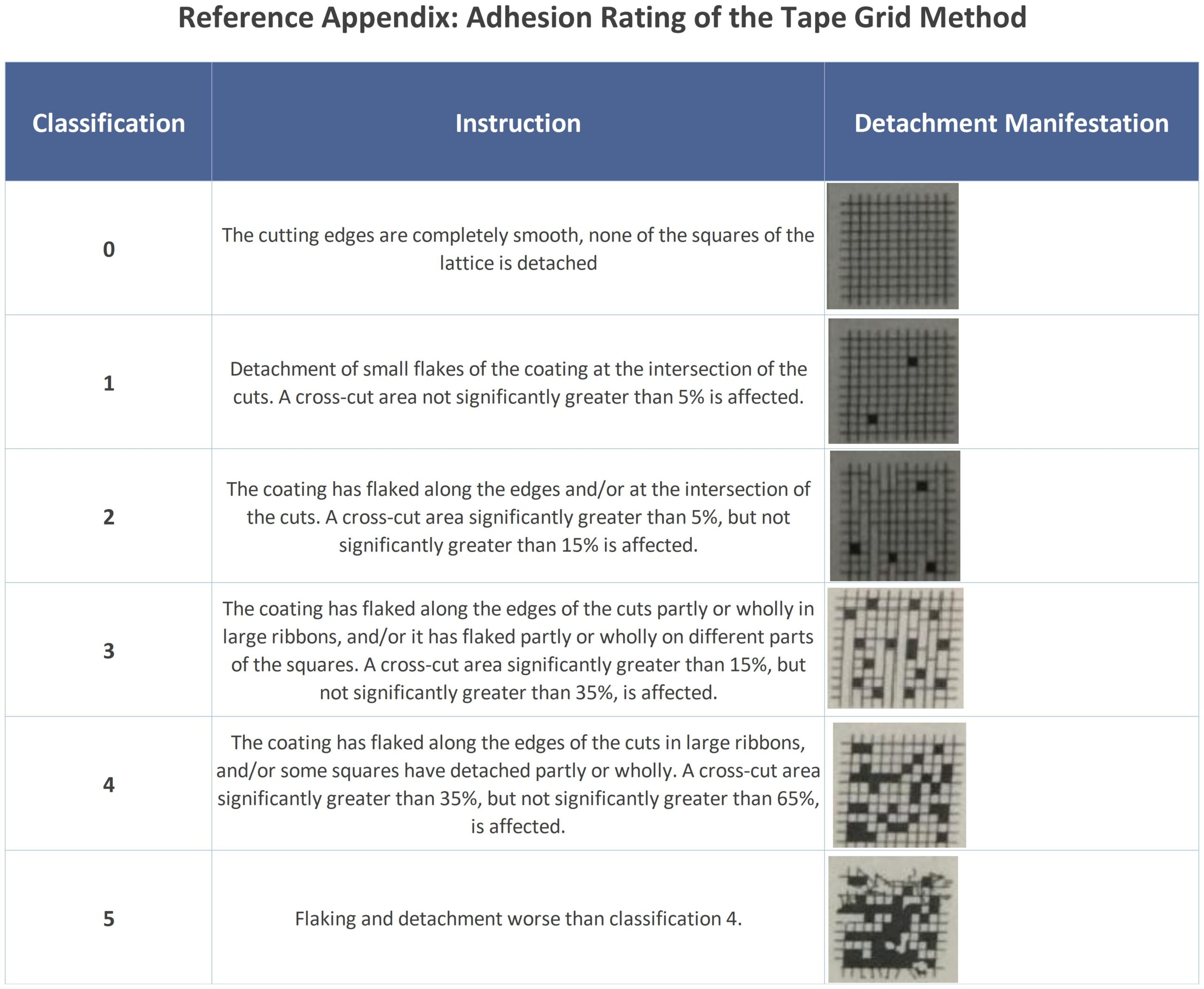
1. Use a sharp single-edged blade tip and a steel ruler or a specialized cross cut template to create 11 parallel scratches on the coating, each 2.4 mm apart and 38 mm long. Then repeat the process in the vertical direction. The blade tip must penetrate the coating down to the metal.
2. Use 3M SCOTCH#897 tape (3M-897) to stick it within the grid area, ensuring the tape’s direction is parallel to a set of scratch lines. Rub the tape with your finger to eliminate any air trapped in the adhesive area and achieve maximum adhesion between the tape and the coating.
3. Hold one end of the tape with your fingers and quickly pull it upward at a 90° angle. Repeat this three times, using a new piece of tape each time.
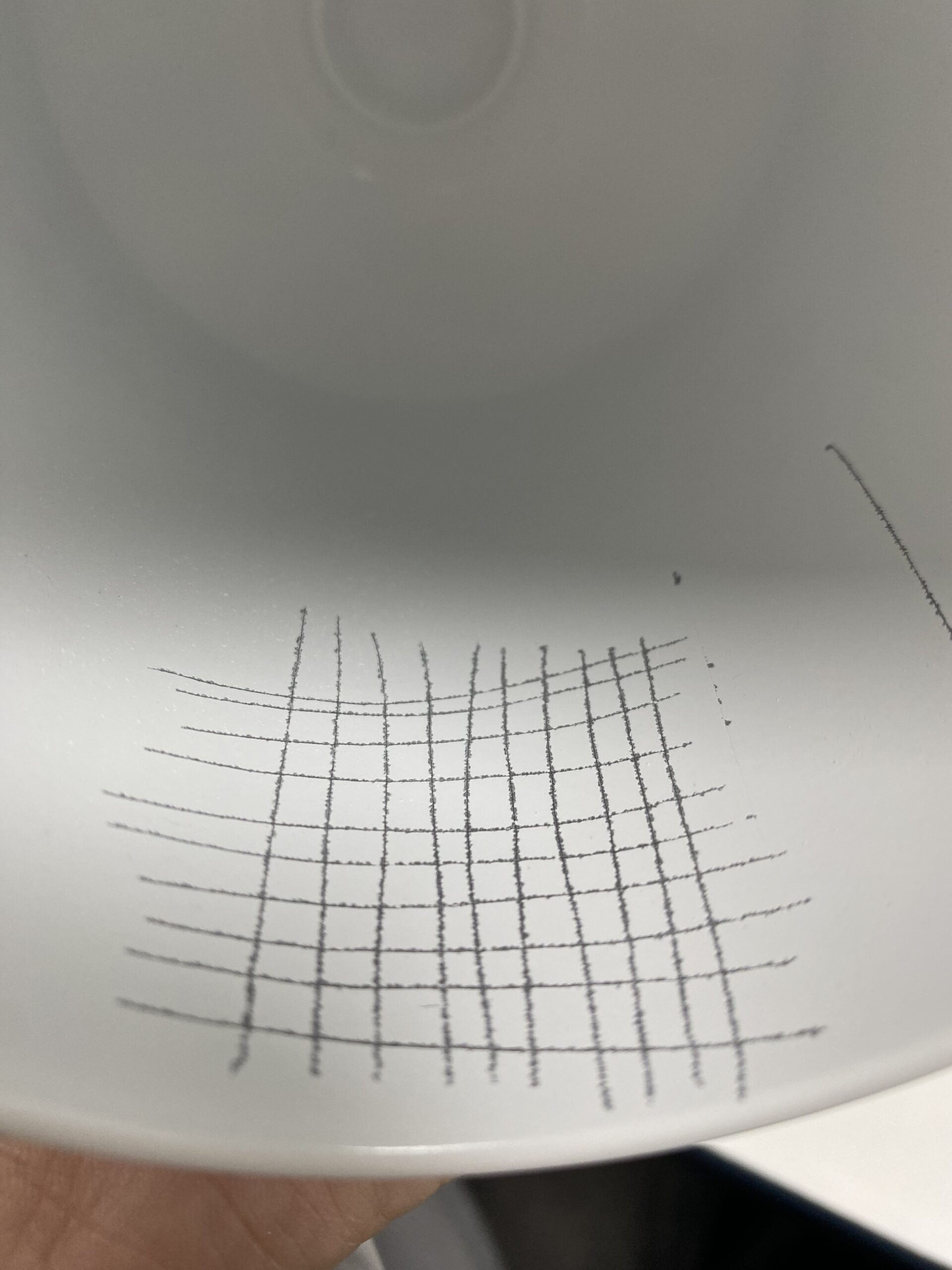
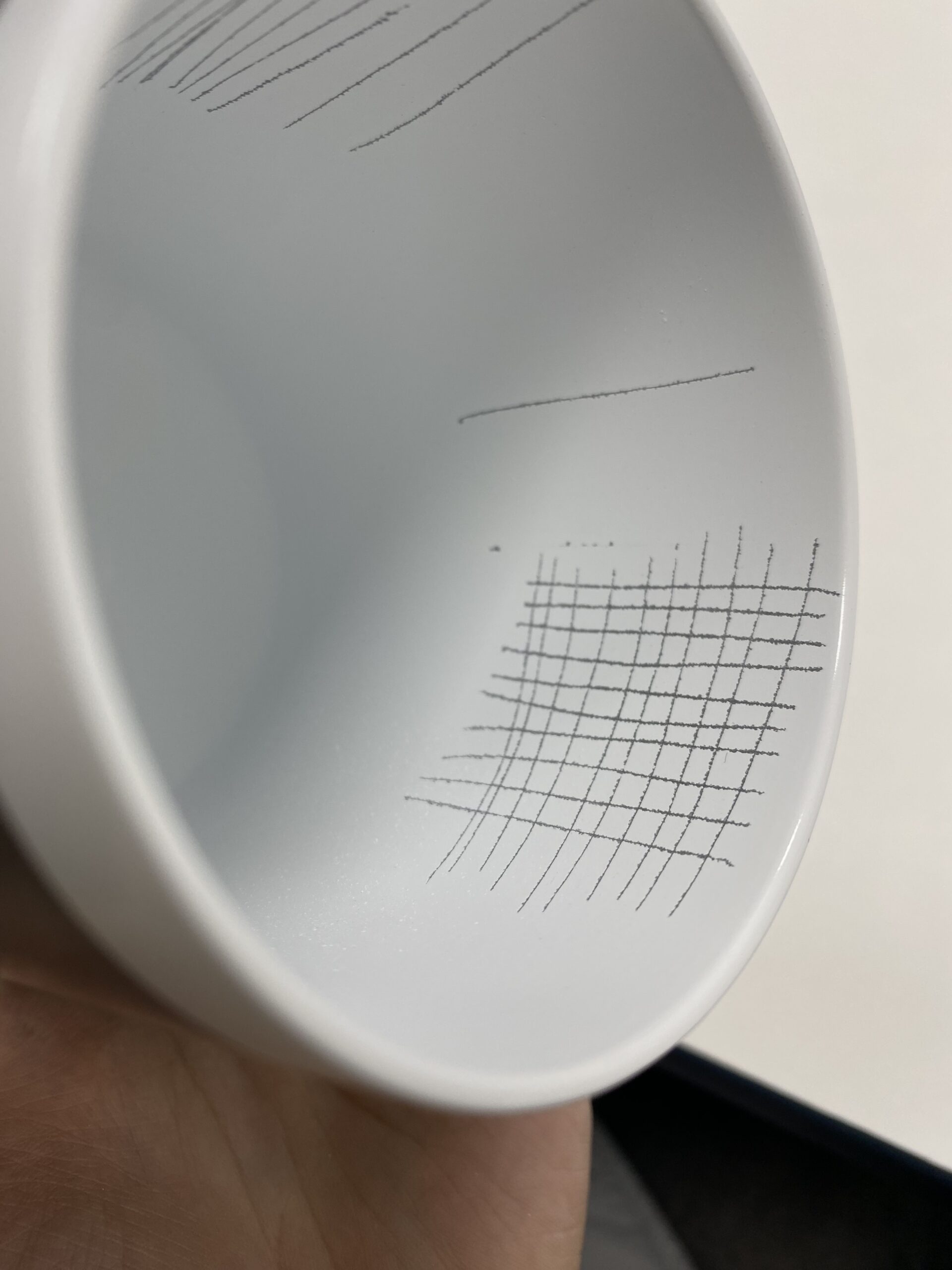


Evaluation and Determination
The coating within the grid area must meet Class 0 standard, with no entire grid peeling off.
Stain Resistance Test
Add ground coffee, 2 spoons of sugar, and 2 spoons of milk crystals to the cup. After 120 hours, pour out the drink, and use a dishcloth to wipe it clean, ensuring no marks remain on the surface.
Make proper test records and save them.
Pencil Hardness Test
Position the coating film facing up, and select a STAEDTLER pencil 6H. Sharpen the pencil to expose about 3mm of lead. Grind the pencil lead at a 90° angle on sandpaper to create a flat tip, ensuring the front edge remains sharp. Hold the pencil at a 45° angle, applying pressure without breaking the lead. Push the pencil across the coating surface at a consistent speed of 1 mm/s for approximately 2.5 cm, scraping along the coating layer. After each pass, re-sharpen the pencil lead’s tip. Repeat the scraping process three times without damaging the paint film.
Impact Resistance Test
1. Place the coated sample flat on a level surface. Drop a 300g ± 1g steel ball vertically from a height of 30cm onto the smooth coating surface. The coating should not show any cracking.
2. After adding 30% ice cubes (based on the size of the ice tray), fill the bottle with water up to 60% and shake vigorously for 1 minute. The coating should not show any damage.
Thermal Shock Test
Fill the cup with boiling water (100°C) to 80% full and cover with the lid for 5 minutes. Afterward, pour out the boiling water and immediately fill the bottle with ice water (0°C) to 80% full, then wait for 5 minutes.







